

This is because a lot of thermal energy is required to break down the inter-ionic forces and form a liquid. Melting and boiling points: These compounds generally have high melting points. Similarly, these compounds conduct electricity in the fused state also. The solution can thus conduct electricity. Instead, they are often hard solids, always made up of ions held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction between ions with opposite charge.Įlectrical conductivity: When added to water, the ions separate. Non-directional nature of ionic bond: These compounds do not exist as individual molecules. High lattice enthalpy (LE) If LE + EGE > IE, an ionic bond is formed. More negative electron gain enthalpy (EGE) The energy change in this process is called lattice enthalpy (∆ latticeH)įactors favouring the formation of ionic bond: The packing of the cation and anion to form an ionic compound. The energy involved in this process is called electron gain enthalpy (∆ egH). The amount of energy required for this process is called ionization enthalpy (∆ iH).įormation of negative ion from the electronegative atom. The formation of a positive ion (cation) from the electropositive atom. Let us take another example of MgCl 2 (Magnesium Chloride):Įnergy changes during the formation of an Ionic Bond:Īn ionic bond formation involves the following steps: The number of electrons lost or gained is known as the electro-valency. These ions are held together by the electrostatic force of attraction. Or, it is the force of attraction between two oppositely charged ions. Ionic bond: A bond formed by the transfer of an electron between 2 atoms is called an ionic or electrovalent bond. Types of Chemical Bonds: The chemical bonds are classified into the following types Central atom has less than 8e –.įormation of hypervalent compounds like PCl 5, SF 6, IF 7, H 2SO 4 in which the central atom has more than 8 electrons.įormation of compounds of noble gases like XeF 2, XeF 4, XeF 6. This is because both are happy with two electrons belonging to the outer shells.įormation of electron-deficient compounds like BeCl 2, BF 3, AlCl 3. Two notable exceptions to the octet rule are helium and hydrogen. Moreover, these atoms can be the same element or with different elements.
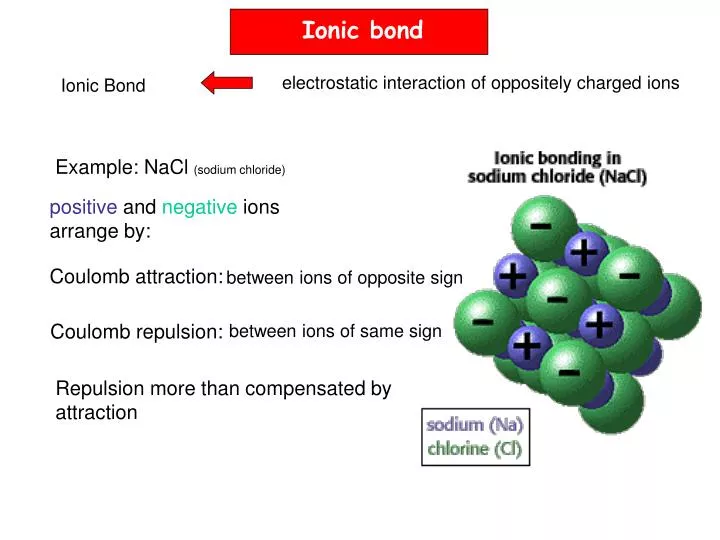
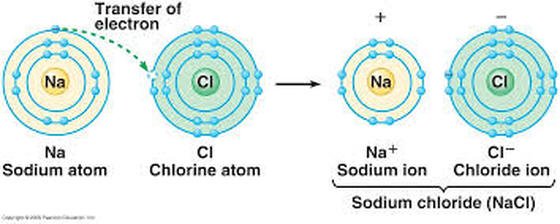
To attain octet, they share electrons or exchange electrons. Furthermore, the atom does this by bonding with each other. Or, atoms containing 8 electrons in their valence shell are stable. According to this rule, atoms undergo chemical reactions in order to attain an octet of electrons in the valence shell. Octet Rule: This rule was proposed by Lewis and Kossel. The inner electrons are well protected and they are called core electrons. The structures are written as the element symbol surrounded by dots that represent the valence electrons. Lewis Dot Structure: It is a shorthand to represent the valence electrons of an atom. The electrons which take part in two or more atoms to complete an octet is known as Electrovalency. The elements with one, two, three, four, five, six, or seven electrons in the outer shell, use these electrons to complete octet. It is formed either by the transfer of electrons or by the sharing of electrons. The attractive force that binds the atoms together in a molecule is called a chemical bond. Such atomic aggregates occur as molecules. They do not exist as single atoms under ordinary conditions. It is observed that the atoms of all the elements, except those for noble gases, tend to remain in a combined state with the atoms of the same or other elements. Ionic bond, Octet rule, properties of ionic bond


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
